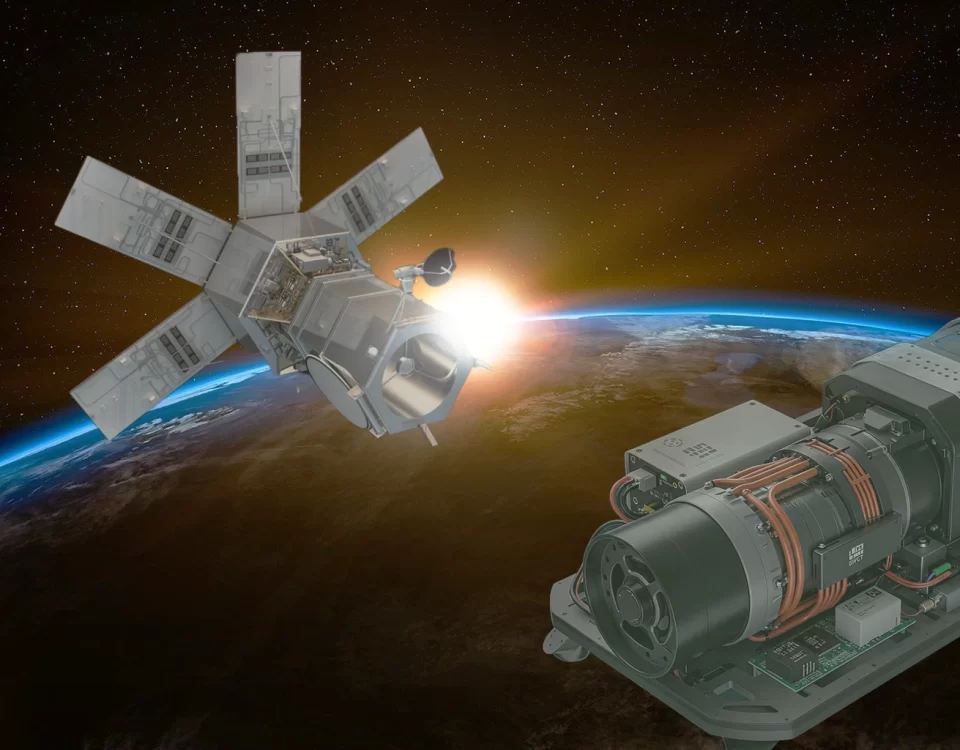
electric propulsion systems for efficient satellite orbit raising
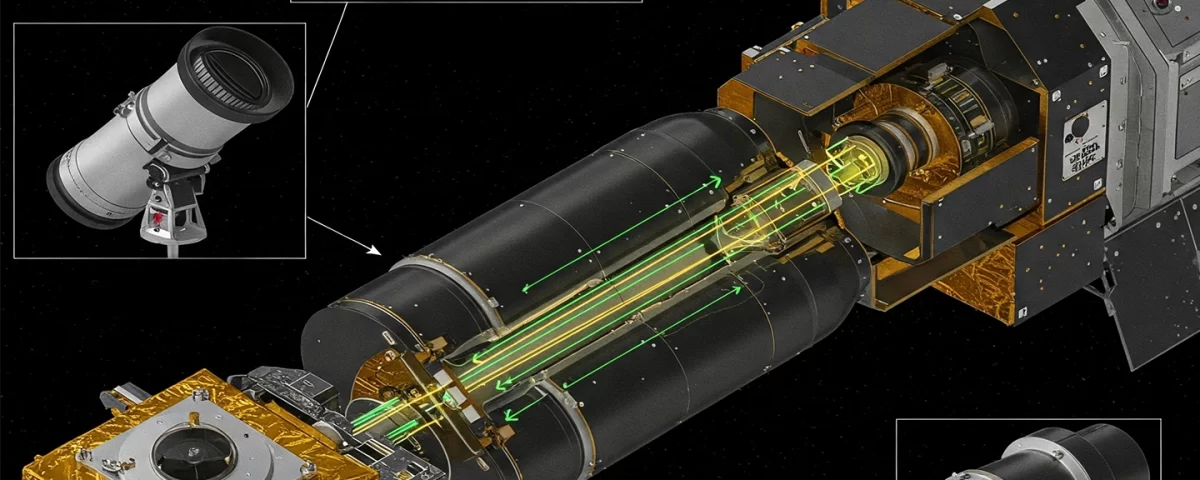
February 17, 2025Optical payloads use light to send, receive, and process information, and they’re much better than old-fashioned electronic systems for certain jobs. They work by using a laser to create light, then changing that light (like its brightness or how its waves move) to encode data. This light is then sent through something like a fiber optic cable or even just through the air. A detector at the other end turns the light back into an electrical signal that can be understood by computers. Optical payloads are made up of things like lasers, light changers (modulators), lenses, and detectors. Because they use light, they can send a lot of data very quickly and aren’t affected by electrical noise, which makes them perfect for things like internet connections, taking pictures from space, medical scans, and scientific experiments.
How do Optical payloads work?
Optical payloads work by using light to transmit information. First, a light source, usually a laser, generates a beam of light. This light is then manipulated, or modulated, to encode data by changing properties like its intensity or phase. This modulated light beam is then transmitted through a medium, which could be optical fiber, free space (like air or a vacuum), or even the atmosphere. At the receiving end, a photodetector converts the light signal back into an electrical signal. This electrical signal is then processed to retrieve the original information. Essentially, optical payloads use light as a carrier wave to transmit data, similar to how radio waves are used in wireless communication, but with much higher frequencies enabling much greater data capacity.
Advantages of Optical payloads
Optical payloads are better than traditional electronic systems in several key ways.
- High Bandwidth and Data Rates: They can send much more data very quickly because light waves, which they use, have a much higher frequency than the signals used in electronics. Think of it like a super-fast highway for information.
- Security: They’re also not bothered by electrical noise, which can disrupt electronic systems, making them more reliable. Because light travels easily through fiber optic cables, optical payloads can send information over long distances without losing much signal strength. This is important for things like internet connections that span continents. It’s also harder for someone to secretly listen in on optical communications, making them more secure.
- Compact and Lightweight: Optical payloads can be made small and light, which is a big plus for satellites or other equipment where size and weight matter. They also often use less power than electronic systems, especially for long distances.
- Versatility: Finally, they’re adaptable and can be used for many different purposes, from communication to taking pictures from space to medical equipment. So, while they might sometimes be more complicated or expensive, optical payloads offer a lot of benefits, especially when speed, reliability, and security are important.
challenges of Optical payload
Even though optical payloads have many benefits, they also have some downsides.
- First, the parts they’re made of, like lasers and lenses, can be really expensive, more so than similar electronic parts. This makes setting up an optical system costly, especially if it’s a special design.
- Second, they’re complicated to build. You need experts in different fields, and getting everything lined up perfectly is tricky and takes time.
- Third, they can be fragile. Things like temperature changes, vibrations, and even humidity can mess them up, so they need special protective packaging, which adds to the cost and complexity.
- Fourth, if you’re sending the light through the air (instead of a fiber optic cable), the signal gets weaker over distance, and things like fog or rain can block it.
- Fifth, while fiber optic cables are good at carrying light, the lasers and other parts still need power, and that can be a problem for some uses.
- Sixth, connecting optical systems to regular electronic systems can be difficult.
- Seventh, making the parts with the needed precision is tough and expensive.
- Eighth, sometimes you can’t just buy the parts you need off the shelf, so you have to have them made, which takes time and money.
- Finally, testing and fixing optical systems is more complicated and requires special tools and skills.
In short, optical payloads are a game-changing technology that can revolutionize many areas. By using light, these advanced systems allow us to send data faster, more reliably, and more efficiently than ever before, pushing the limits of communication, sensing, and information processing. Although there are still some hurdles to overcome, ongoing improvements in technology are making optical payloads more common, promising a bright future. From space exploration to medical advancements, optical payloads are set to become even more important in how we understand the world and develop new technologies.